Sexual hormones in HIV-infected patients: the influence of antiretroviral therapy
Collazos, Julio; Martinez, Eduardo; Mayo, José; Ibarra, Sofia
Section of Infectious Diseases, Hospital de Galdakao, Vizcaya, Spain.
Received: 3 August 2001;
revised: 16 November 2001; accepted: 26 November 2001.
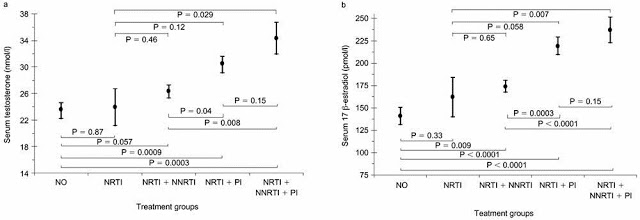
A total of 351 determinations of sexual hormones were carried out in 189 HIV-infected men in stable clinical condition. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) was associated with increased levels of both testosterone and 17β-estradiol, but not with luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Protease inhibitors were more associated with testosterone, and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors with 17β-estradiol. The values of both hormones, but not those of LH and FSH, increased with respect to pre-treatment levels in those patients who initiated HAART.
More Information
Higher estradiol in HIV has been associated with gynecomastia (breast enlargement) in a minority of men on non-nucleoside analog HIV medications:
HIV medication induced gynecomastia